Starch & protein
PROTEINS

Beyond vegetable protein concentrates and plant isolates, we also offer complete solutions for hydrolyzed fish and animal proteins, including gelatins.
GEA has developed a comprehensive range of technologies, equipment and know-how to configure and install equipment for key process steps in vegetable protein manufacturing.
Key process steps for plant-based protein powders
-
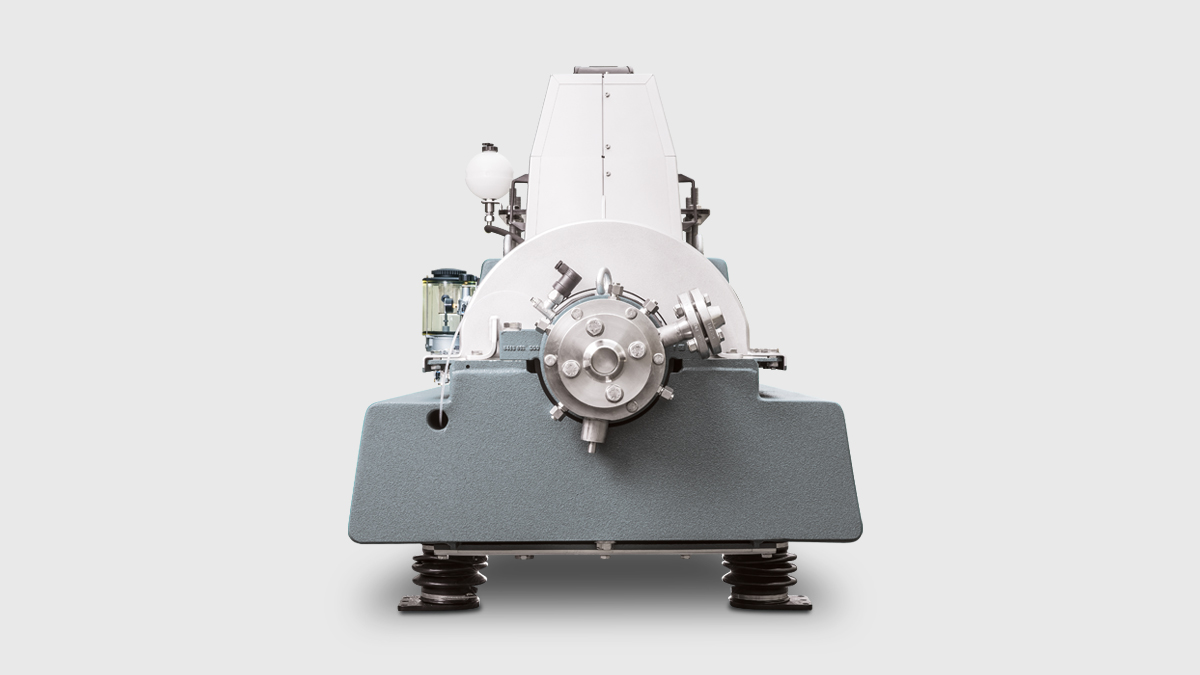
1. Protein extraction and purification
The most common wet separation is a multi-stage process involving protein extraction, protein precipitation and purification. Key end points are consistent protein quality and high yields, using technologies that ensure hygienic processing and sustainable water management. A membrane filtration unit could optionally be used to isolate specific fractions of the purified protein.

-
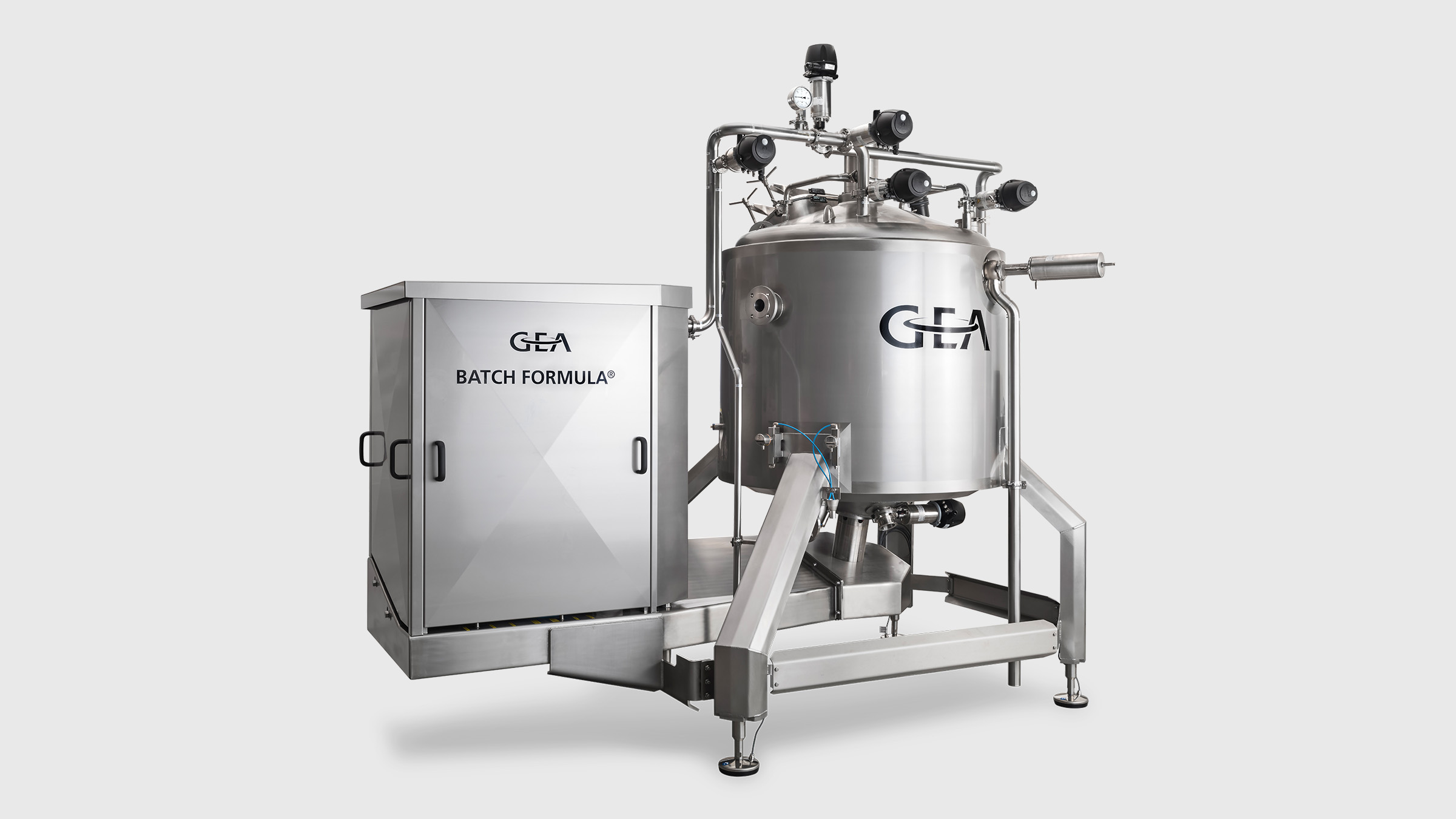
2. Neutralization
The protein-rich fraction derived from the isolation and purification steps is neutralized and diluted to the required concentration and viscosity.

-
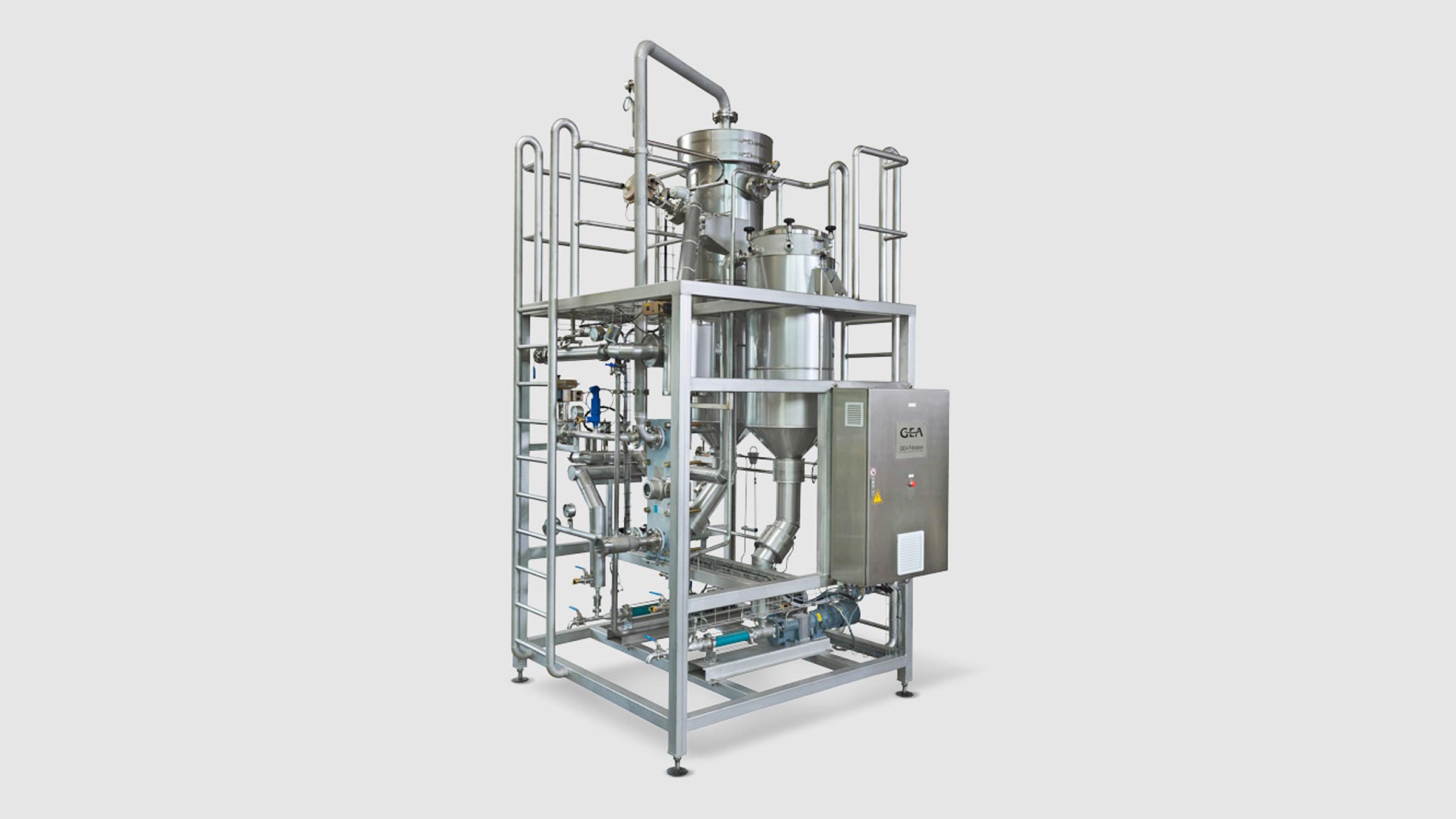
3. Heat treatment
An indirect UHT plant with tube heat exchanger, steam injection or steam infusion is used to carry out effective heat treatment of protein dispersions.

-
4. Protein drying
The dryer is configured to match the final protein powder properties. The configuration can vary from single stage to three stage drying, with or without fines recycling, integrated agglomeration and/or lecithination.
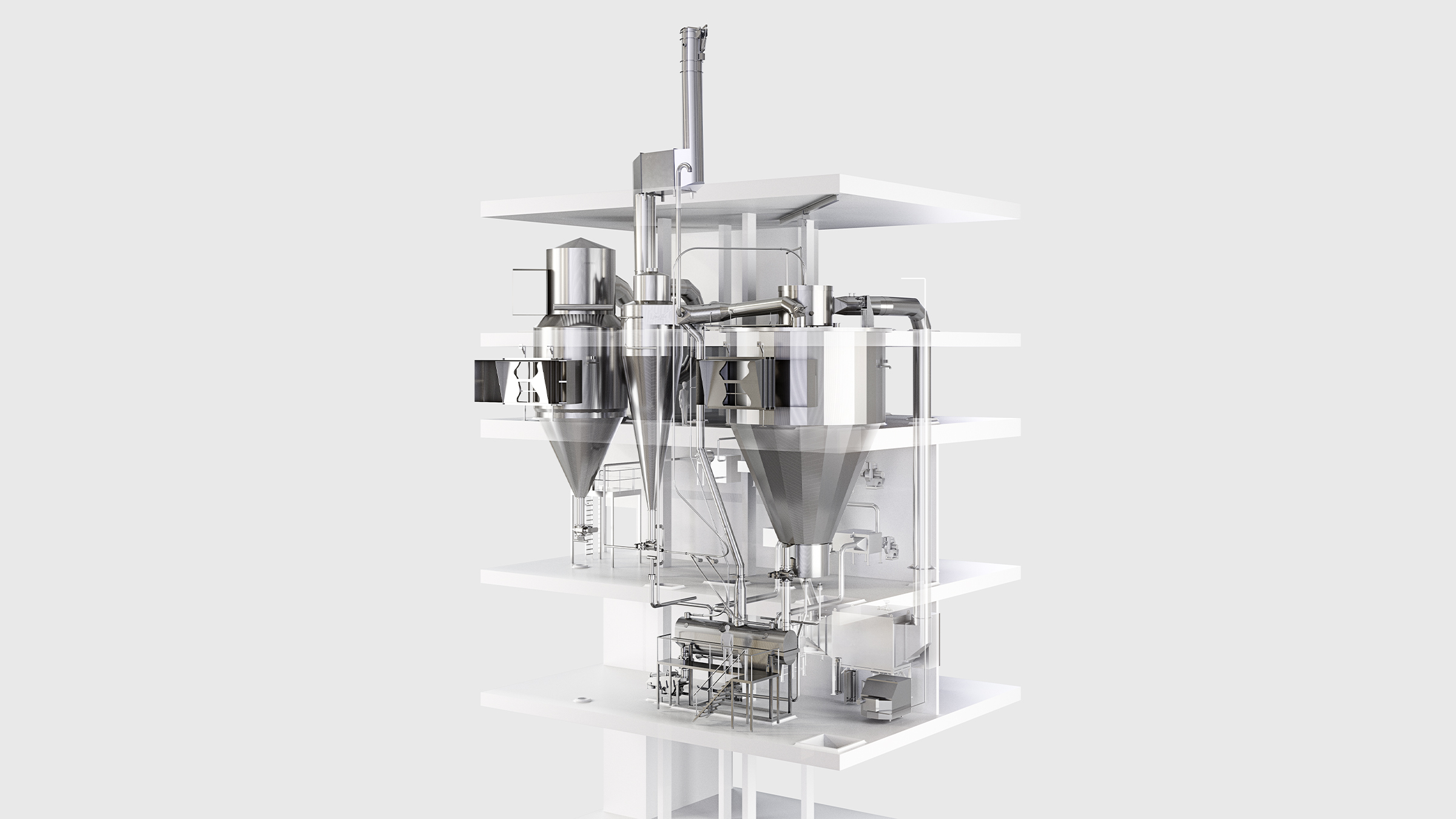

-
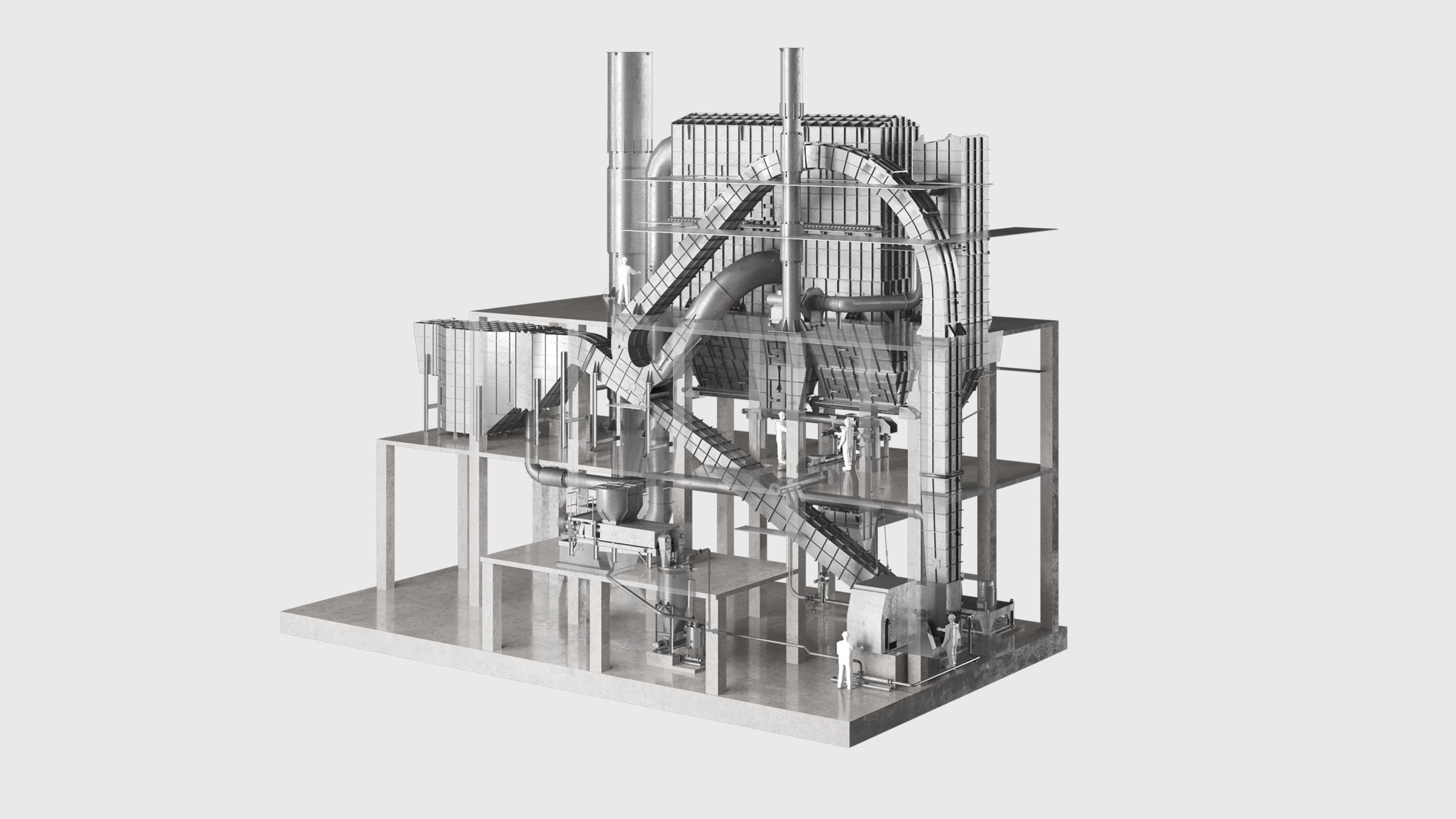
5. Starch and fiber drying
Flash and ring dryers are used for starch and fiber streams drying. Wet material is dispersed into a stream of heated air, which conveys it through a drying column. The heat from the air stream dries the material as it is conveyed.
-
6. Powder handling
Conveying of powder from the dryer to powder storage followed by conveying to the powder filling system or other processing unit such as powder mixing. Conveying can be performed by gravity, pneumatic, mechanical or vibratory means as required by the application.
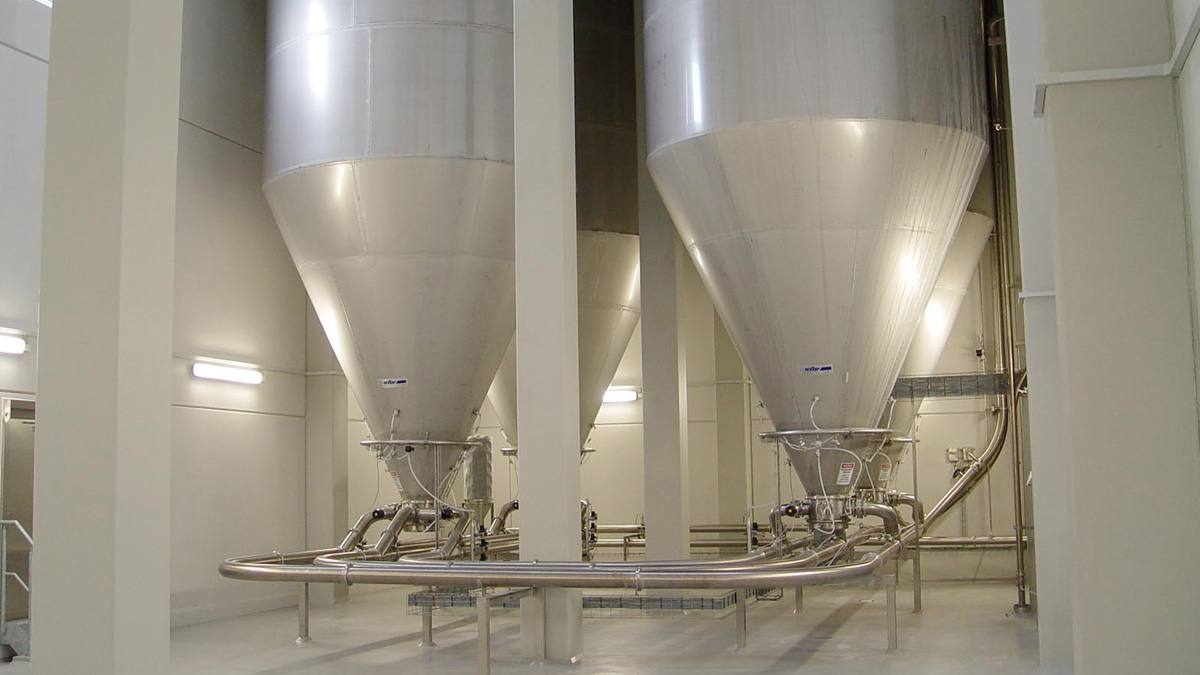

-
7. Powder filling
Powder filling into 25kg and big bags using high hygiene automatic powder fillers. Automated bag handling and closing is performed inside an enclosed safe environment to eliminate potential for contamination.
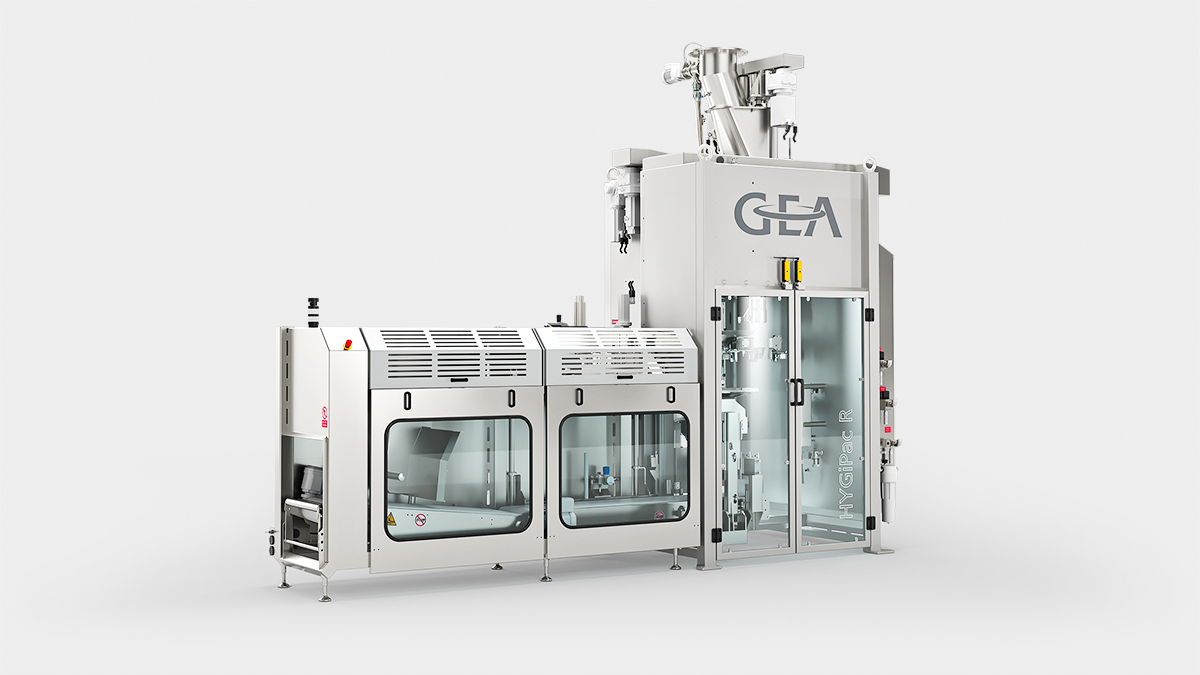

-
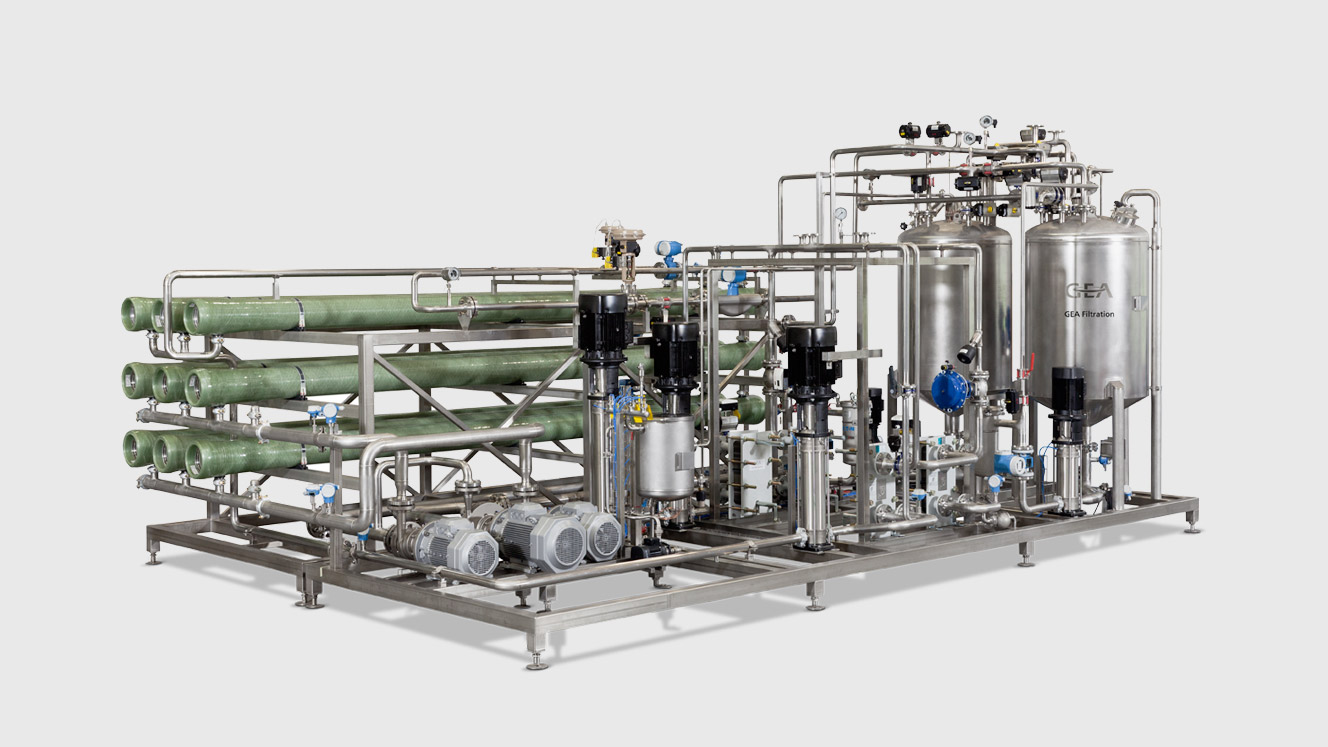
8. Effluent treatment
Effluent from the protein isolation process can undergo thermal separation in an evaporator, to produce a concentrate and a clean condensate. Condensate from the evaporator can be further purified in a GEA reverse osmosis (RO) plant to generate a concentrated retentate and a permeate of very high purity.

-
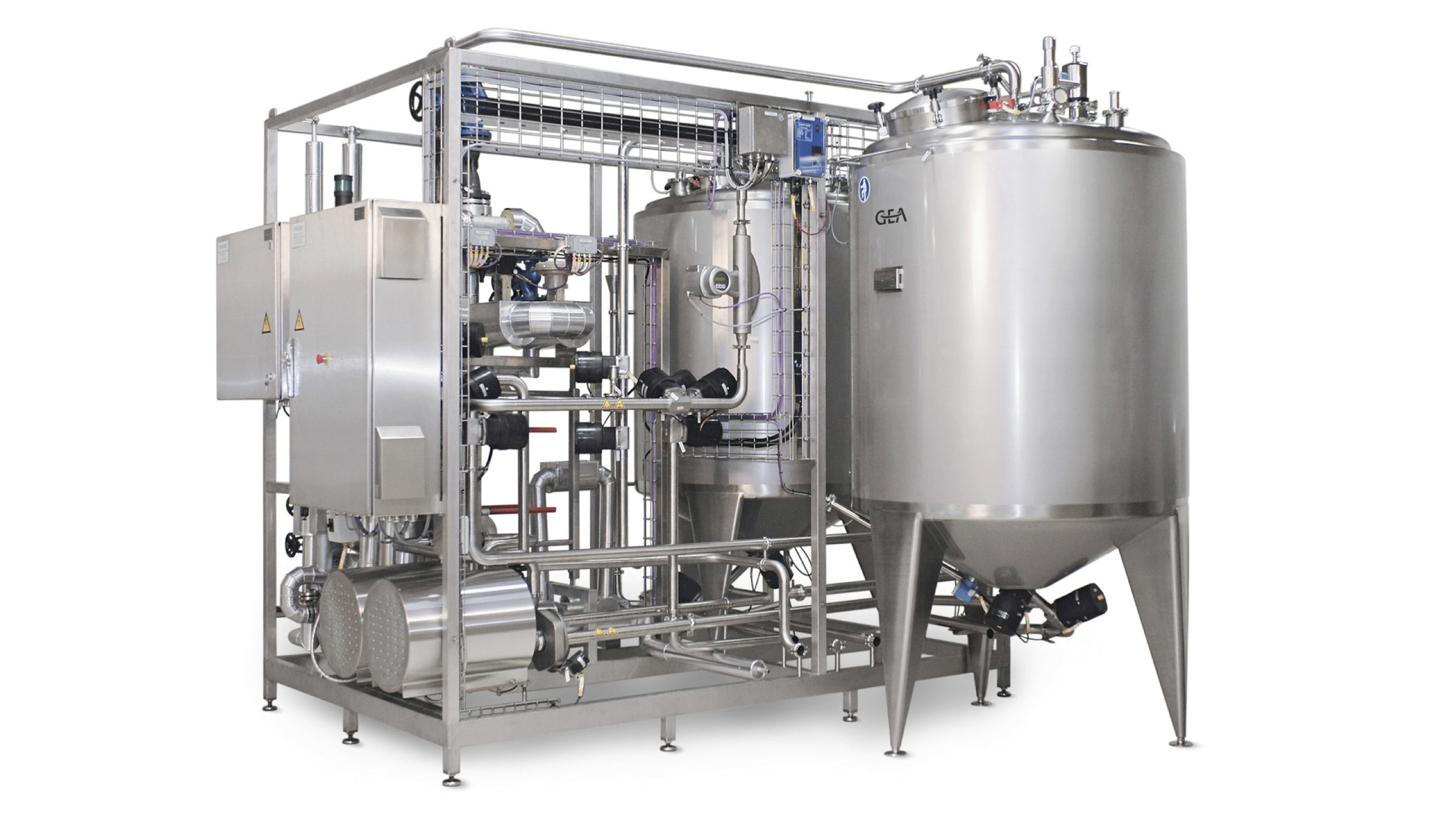
9. CIP/SIP
Effective CIP solutions remove any leftover product from the plant, tank surfaces, heat exchangers, pumps, pipes, etc. Systems with SIP (Sterilize-in-Place) functionality for high microbiologic control can be integrated.

-
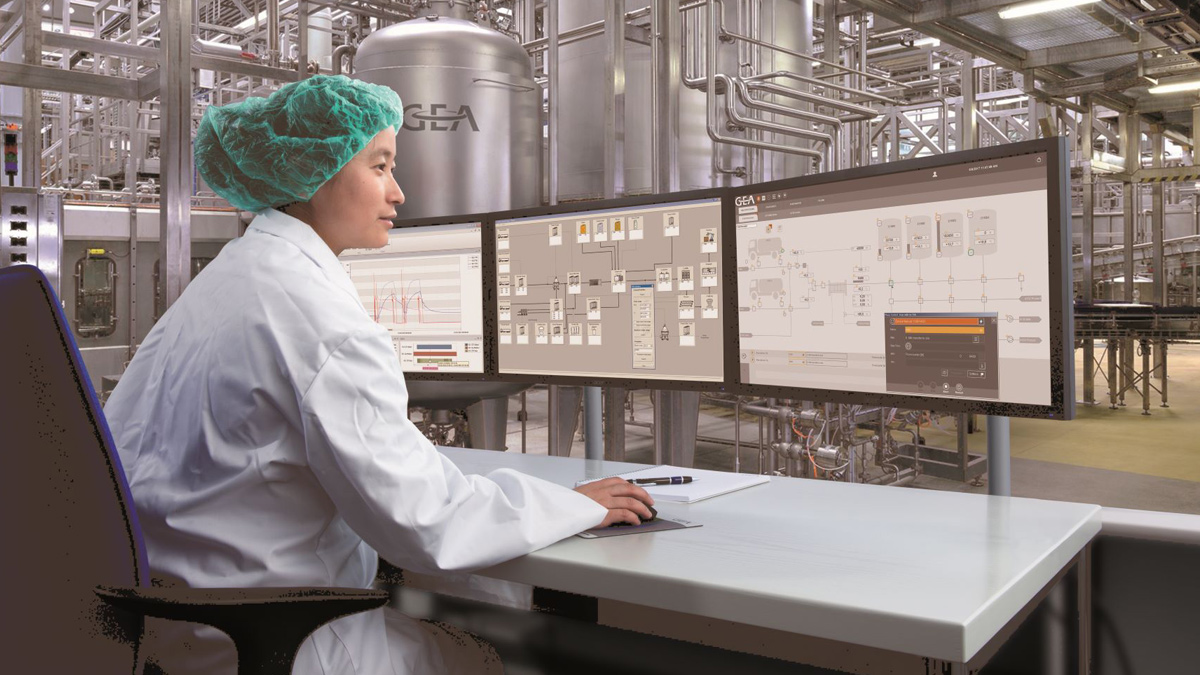
10. Automation
Advanced process control tools enable consistent, and robust process conditions with the highest efficiency levels and minimum energy consumption.

-
1. Protein extraction and purification
The most common wet separation is a multi-stage process involving protein extraction, protein precipitation and purification. Key end points are consistent protein quality and high yields, using technologies that ensure hygienic processing and sustainable water management. A membrane filtration unit could optionally be used to isolate specific fractions of the purified protein.

-
3. Heat treatment
An indirect UHT plant with tube heat exchanger, steam injection or steam infusion is used to carry out effective heat treatment of protein dispersions.

-
5. Starch and fiber drying
Flash and ring dryers are used for starch and fiber streams drying. Wet material is dispersed into a stream of heated air, which conveys it through a drying column. The heat from the air stream dries the material as it is conveyed.

-
7. Powder filling
Powder filling into 25kg and big bags using high hygiene automatic powder fillers. Automated bag handling and closing is performed inside an enclosed safe environment to eliminate potential for contamination.

-
9. CIP/SIP
Effective CIP solutions remove any leftover product from the plant, tank surfaces, heat exchangers, pumps, pipes, etc. Systems with SIP (Sterilize-in-Place) functionality for high microbiologic control can be integrated.

-
2. Neutralization
The protein-rich fraction derived from the isolation and purification steps is neutralized and diluted to the required concentration and viscosity.

-
4. Protein drying
The dryer is configured to match the final protein powder properties. The configuration can vary from single stage to three stage drying, with or without fines recycling, integrated agglomeration and/or lecithination.

-
6. Powder handling
Conveying of powder from the dryer to powder storage followed by conveying to the powder filling system or other processing unit such as powder mixing. Conveying can be performed by gravity, pneumatic, mechanical or vibratory means as required by the application.

-
8. Effluent treatment
Effluent from the protein isolation process can undergo thermal separation in an evaporator, to produce a concentrate and a clean condensate. Condensate from the evaporator can be further purified in a GEA reverse osmosis (RO) plant to generate a concentrated retentate and a permeate of very high purity.

-
10. Automation
Advanced process control tools enable consistent, and robust process conditions with the highest efficiency levels and minimum energy consumption.

Products & technologies
-
Showing 1 of 1Centrifuges & Separation EquipmentSince 1893, GEA has been building centrifuges which combine high separating efficiencies, clarifying efficiencies and throughput capacities with maximum savings in terms of energy, water and disposal costs.
Let's stay in touch!
Contact us


